For cross OS compatibility, ⌘ and ctrl are equivalent.
Installation
Quick Start
Define your keybindings config.
import { parseKeybindingsConfig } from "@kit/keybindings/config"; import { dashboardRoutes } from "@kit/shared/config/routes"; export const keybindingsModel = parseKeybindingsConfig({ // Navigation "navigation.home": { name: "Go to Home", description: "Navigate to home page", defaultShortcut: "ctrl+h", context: "global", url: dashboardRoutes.paths.dashboard.slug.index, }, "navigation.settings": { name: "Go to Settings", description: "Navigate to settings page", defaultShortcut: "ctrl+j", context: "global", url: dashboardRoutes.paths.dashboard.slug.settings.index, }, // UI "ui.toggleTheme": { name: "Toggle Theme", description: "Switch between light and dark theme", defaultShortcut: "ctrl+shift+l", context: "global", }, "ui.toggleSidebar": { name: "Toggle Sidebar", description: "Show/hide sidebar", defaultShortcut: "ctrl+b", context: "global", }, });
Avoid system shortcuts (Cmd+Q, Cmd+W, etc.)
Implement the keybinding actions.
Do not implement the actions beginning with navigation. here. Declarations inconfig/keybindings.config.ts will automatically implement it.
"use client"; import { useKeybinding } from "@kit/keybindings/ui"; import { useTheme } from "next-themes"; export function KeybindingsHandlers() { const { theme, setTheme } = useTheme(); useKeybinding("ui.toggleTheme", () => { const newTheme = theme === "dark" ? "light" : "dark"; setTheme(newTheme); }); useKeybinding("ui.toggleSidebar", () => { const sidebarToggle = document.querySelector( '[data-sidebar-toggle], [data-sidebar="trigger"], .sidebar-toggle', ) as HTMLButtonElement; if (sidebarToggle) { sidebarToggle.click(); } }); return null; }
Congratulations! Now you can start using your keybindings.
Display Keybindings
Use the KeybindingDisplay component to display the keybindings.
"use client"; import { KeybindingDisplay } from "@kit/keybindings/ui"; import { Muted } from "@kit/ui/text"; import { keybindingsModel } from "~/config/keybindings.config"; export default function YourApp() { return ( <div className="flex flex-col items-center gap-2"> <Muted> Press{" "} <span className="text-black capitalize dark:text-white"> <KeybindingDisplay actionSlug="ui.toggleTheme" /> </span>{" "} to toggle theme </Muted> <Muted> Press{" "} <span className="text-black capitalize dark:text-white"> <KeybindingDisplay actionSlug="ui.alert" /> </span>{" "} to alert </Muted> </div> ); }
Use it in your navigation/menu components to display the keybindings.
User customizations
Use the KeybindingsTable component to let users customize shortcuts.
"use client";
import { keybindingsModel } from "~/config/keybindings.config";
import { KeybindingsTable } from "@kit/keybindings/ui";
export default function YourApp() {
return <KeybindingsTable />;
}Typescript support
@kit/keybindings provides a type inference for the keybindings actions.
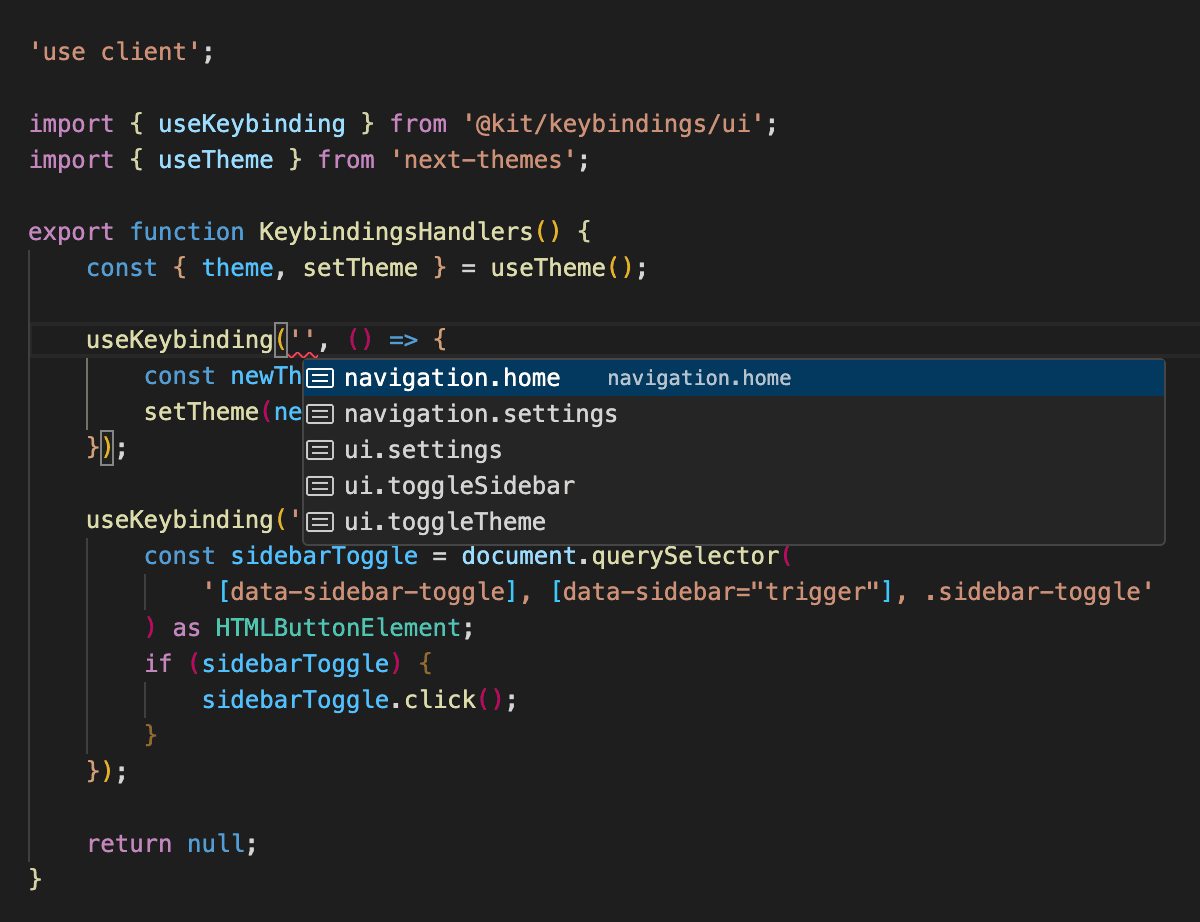
Keybindings typescript autocompletion
Follow this steps to enable the typescript support in a @app/your-app application :
Create a @types folder at the root of the package and create a
keybindings.d.ts file inside it.
Copy paste the following code into the @types/keybindings.d.ts file.
import "@kit/keybindings/ui"; import { KeybindingDisplay as KeybindingDisplayBase, useKeybinding as useKeybindingBase, useShortcut as useShortcutBase, } from "@kit/keybindings/ui/without-context"; import { keybindingsModel } from "../config/keybindings.config"; declare module "@kit/keybindings/ui" { declare const useKeybinding = ( ...params: Parameters<typeof useKeybindingBase<typeof keybindingsModel>> ) => useKeybindingBase<typeof keybindingsModel>(...params); declare const useShortcut = ( ...params: Parameters<typeof useShortcutBase<typeof keybindingsModel>> ) => useShortcutBase<typeof keybindingsModel>(...params); declare const KeybindingDisplay = ( props: React.ComponentProps< typeof KeybindingDisplayBase<typeof keybindingsModel> >, ) => KeybindingDisplayBase<typeof keybindingsModel>(props); }
Add the following typeRoots attribute to the tsconfig.json file.
{
"extends": "@kit/tsconfig/base.json",
"compilerOptions": {
"typeRoots": ["./node_modules/@types", "./@types"]
// ...
}
}API Reference
Components
KeybindingDisplay- Component to display shortcuts
KeybindingDisplayProps
| Prop | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
actionSlug* | keyof T & string |
KeybindingsProvider- Context provider for keybindings
KeybindingsProviderProps
| Prop | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
model* | T | |
storage | KeybindingsStorage | |
children* | React.ReactNode | |
navigationUrlTransformers | ((url: string) => string)[] |
KeybindingsTable- Settings table for editing keybindings
KeybindingsTableProps
| Prop | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
filter | "global" | "contextual" |... | |
className | string | |
initialKeybindings | Record<string, string> | |
isLoading | boolean | false |
Hooks
useKeybinding(actionId, callback, options?)- Register shortcut handleruseKeybindings()- Access keybindings contextuseShortcut(actionId)- Get current shortcut for action
Why the settings package is so powerful.
Guide users through keybindings storage options.
How is this guide?
Last updated on 2/27/2026