Translations
Boost accessibility and reach a wider audience by translating your app into multiple languages.
This feature is implemented in the @kit/i18n package.
This feature is implemented in all the applications of the kit. By default, no setup is needed.
The following steps describe how to implement translations inside a new application.
Setup
Installation
Configuration file
Create a new file config/i18n.config.ts with the following content:
import { parseI18nConfig } from "@kit/i18n/config"; import { DEFAULT_LANG, SUPPORTED_LANGS, } from "@kit/shared/config/defined-languages"; import { applyCrossEnvAsyncFilter, applyCrossEnvFilter, } from "@kit/utils/filters/cross-env"; import { initCrossEnvFilters } from "~/lib/init-cross-env-filters"; initCrossEnvFilters(); async function i18nResolver(language: string, namespace: string) { const serverTranslations = await applyCrossEnvAsyncFilter( "cross_env_get_translations", null, { language, namespace, }, ); if (serverTranslations) { return serverTranslations; } const data = await import(`../public/locales/${language}/${namespace}.json`); return data as Record<string, string>; } const ns = applyCrossEnvFilter("cross_env_get_namespaces", [ "dashboard", "ai-content", "tour", "onboarding", "settings", ]); export const i18nConfig = parseI18nConfig({ defaultLanguage: DEFAULT_LANG, languages: SUPPORTED_LANGS, namespaces: ns, resolver: i18nResolver, });
I18nConfig
| Prop | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
defaultLanguage* | string | |
languages* | string[] | |
namespaces | string[] | |
useRouting | boolean | false |
resolver* | Resolver |
Proxy
import { i18nProxy } from "@kit/i18n/www/proxy";
import { NextResponse, type NextRequest } from "next/server";
import { i18nConfig } from "./config/i18n.config";
export async function proxy(
request: NextRequest,
): Promise<NextResponse<unknown>> {
const response = NextResponse.next();
return await i18nProxy(request, response, i18nConfig);
}
export const config = {
matcher: ["/((?!_next/static|_next/image|images|locales|assets|api/*).*)"],
};Server instance
import { cache } from "react";
import { createI18nServerInstance } from "@kit/i18n/www/server";
import { i18nConfig } from "~/config/i18n.config";
export const getServerI18n = cache(() => createI18nServerInstance(i18nConfig));getServerI18n returns an i18n instance that you can use server-side. See the server-side section for more details.
Add a provider
import React from "react"; import { getServerI18n } from "~/lib/i18n.server"; import { I18nProvider } from "@kit/i18n/shared/provider"; import { i18nConfig } from "~/config/i18n.config"; export default async function RootLayout({ children, }: React.PropsWithChildren): Promise<React.JSX.Element> { // load the language from the server const { language } = await getServerI18n(); return ( <html lang={language}> <body> <I18nProvider config={i18nConfig} lang={language}> {children} </I18nProvider> </body> </html> ); }
Package translations
We support monorepo package translations.
It exists two ways to manage translations for packages inside a monorepo :
-
- Use a different i18n instance in each packages.
-
- Share package translations with the main application i18n instance.
It exists different pros and cons for each approach.
| Approach | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| New i18n instance | - No setup in the consuming application. | - Hard to initialize and synchronize all i18n instances. - The package i18n instance must be used for each translations. |
| Share translations | - No extra setup in the package. | - We must install package translations in the application via the configuration file. |
For those reasons, we are using the second approach.
Translations installation
All the packages exposing a /i18n endpoints own translations.
Here is an example with the @kit/auth package.
By convention:
/i18nprovide the namespace name./i18n/localesprovide the translations files.
import { I18N_AUTH_NAMESPACES } from "@kit/auth/i18n"; import { parseI18nConfig } from "@kit/i18n/config"; import { DEFAULT_LANG, SUPPORTED_LANGS, } from "@kit/shared/config/defined-languages"; async function i18nResolver(language: string, namespace: string) { if (I18N_AUTH_NAMESPACES.includes(namespace as "auth")) { const data = await import( // relative path to the package translations `../../../kit/auth/src/i18n/locales/${language}/${namespace}.json` ); return data as Record<string, string>; } const data = await import(`../public/locales/${language}/${namespace}.json`); return data as Record<string, string>; } export const i18nConfig = parseI18nConfig({ defaultLanguage: DEFAULT_LANG, languages: SUPPORTED_LANGS, namespaces: ["common", ...I18N_AUTH_NAMESPACES], resolver: i18nResolver, });
Add new languages
Let's say you want to add the language fr (french).
Update the SUPPORTED_LANGS constant.
You have to update the languages array in the config files.
To do this, update the SUPPORTED_LANGS constant inside the @kit/i18n package.
export const SUPPORTED_LANGS = ["en", "fr"] as const;Add json translation files inside all the locales folders.
Translate :
- your application json files.
- the json translation files from the packages used by your application.
We advise you to use an AI agent to translate your application.
Typescript support
i18next provide a type inference for the translations. Check the i18next typescript documentation for more details.
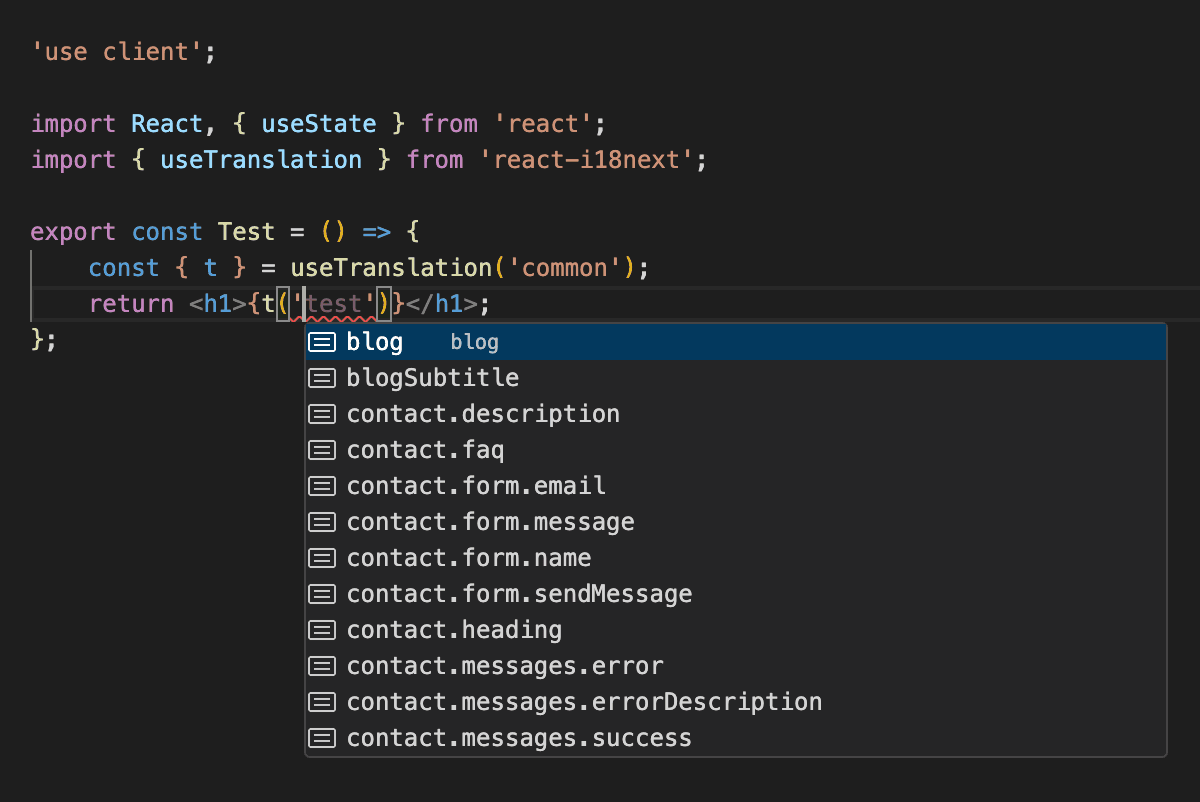
i18next typescript autocompletion
Follow this steps to enable the typescript support in a @kit/dummy package :
Create a @types folder at the root of the package and create a i18n.d.ts
file inside it.
Copy paste the following code into the @types/i18n.d.ts file.
import "i18next";
import enExample from "../src/i18n/locales/en/example.json";
declare module "i18next" {
interface CustomTypeOptions {
defaultNS: "example";
resources: {
example: typeof enExample;
// ... other namespaces
};
}
}Add the following typeRoots attribute to the tsconfig.json file.
{
"extends": "@kit/tsconfig/base.json",
"compilerOptions": {
"typeRoots": ["./node_modules/@types", "./@types"]
// ...
}
}What's next ?
Tools to monitor your application, to track errors and events.
Learn how to use the translations in your application.
How is this guide?
Last updated on 2/27/2026